Ketogenic Diet
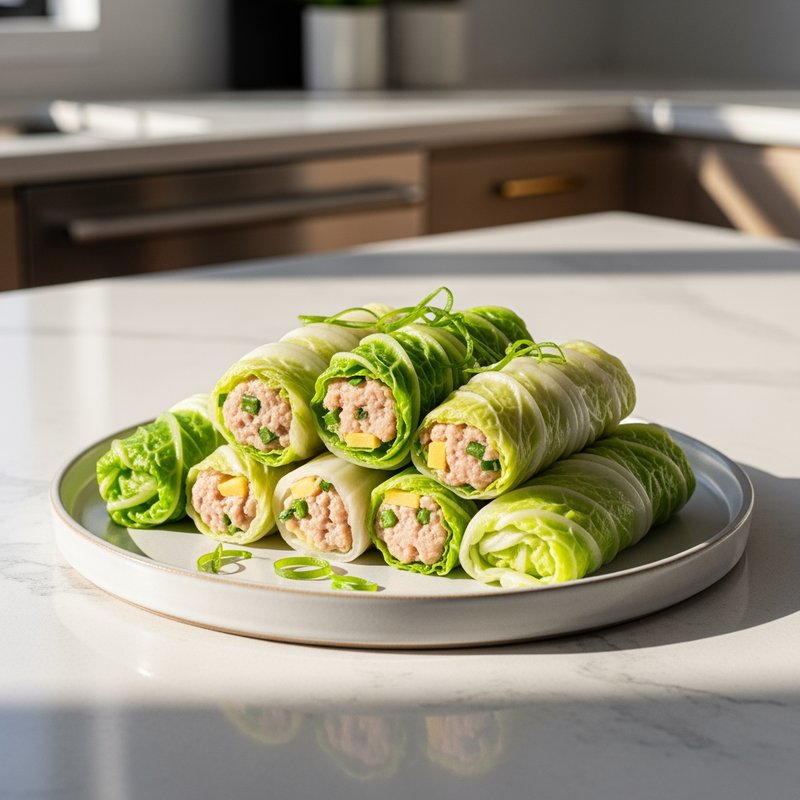
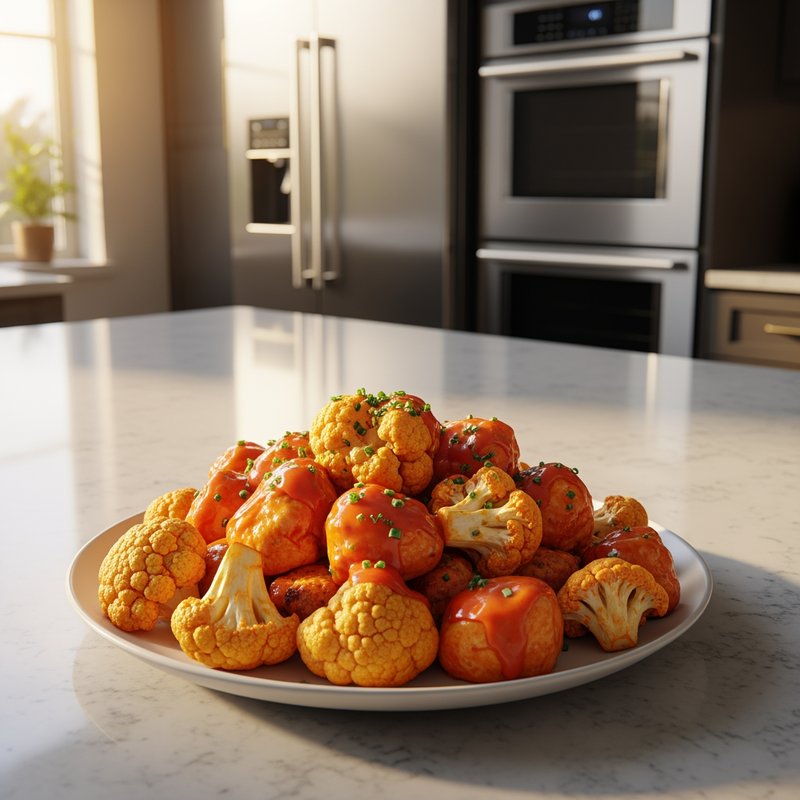
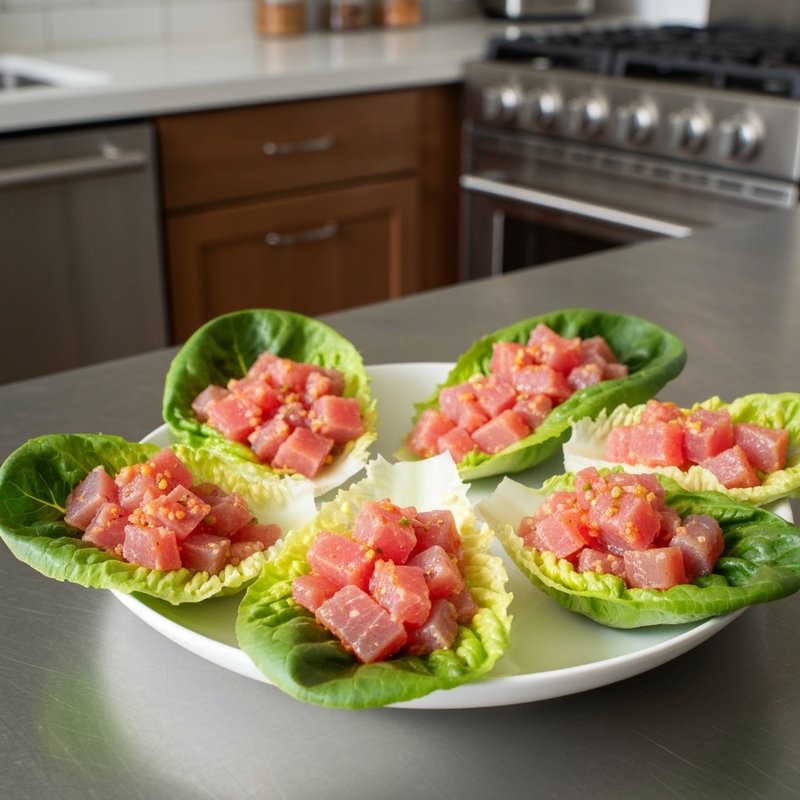
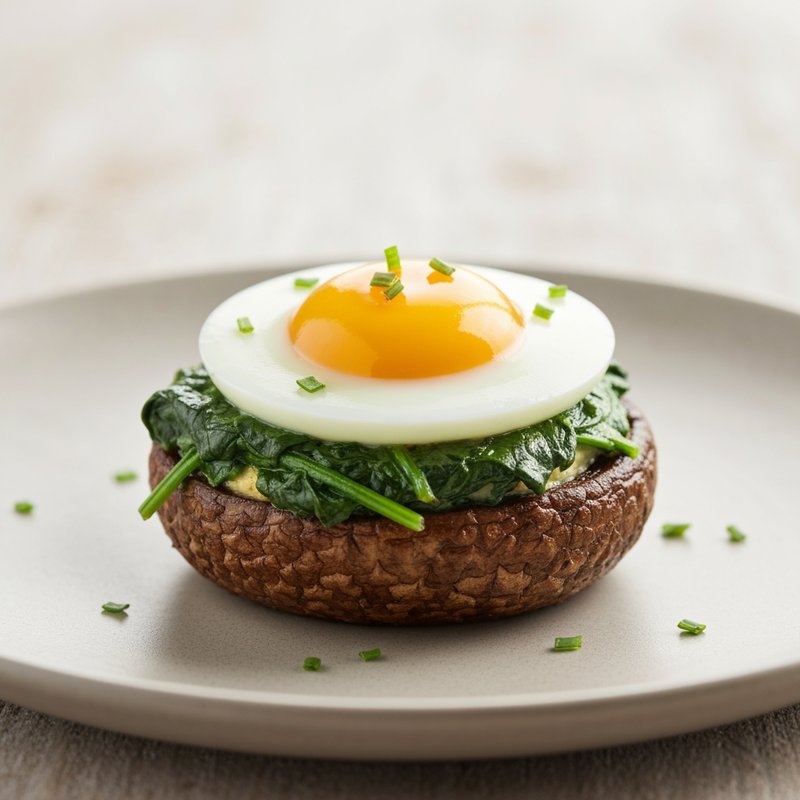
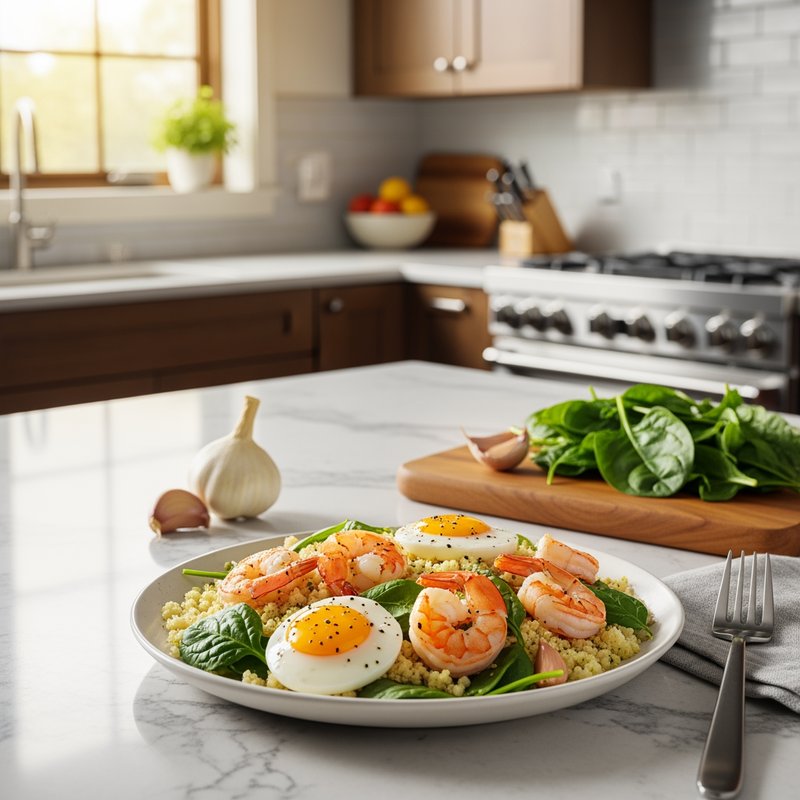
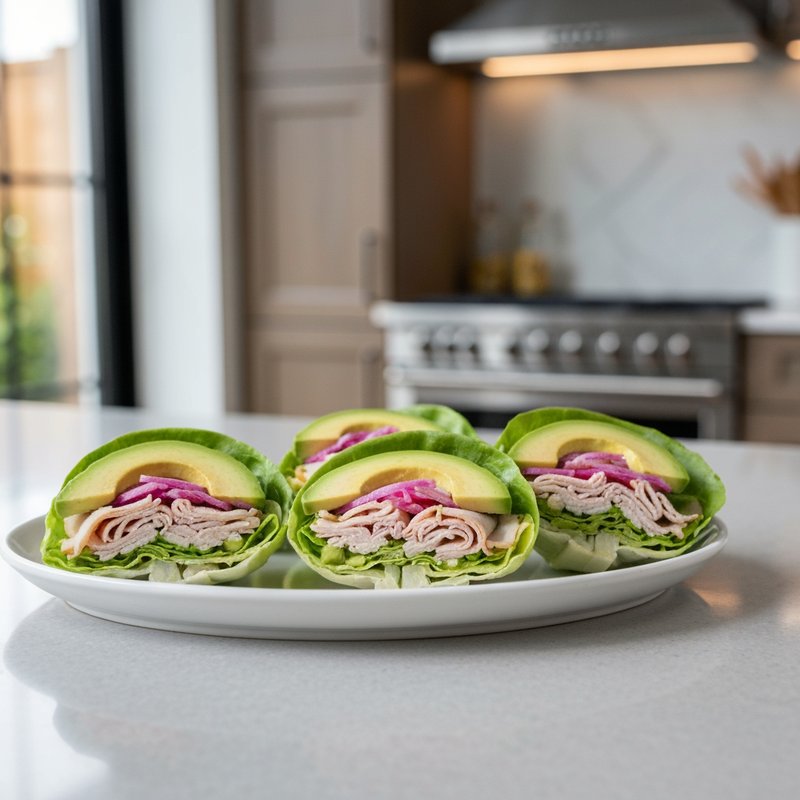
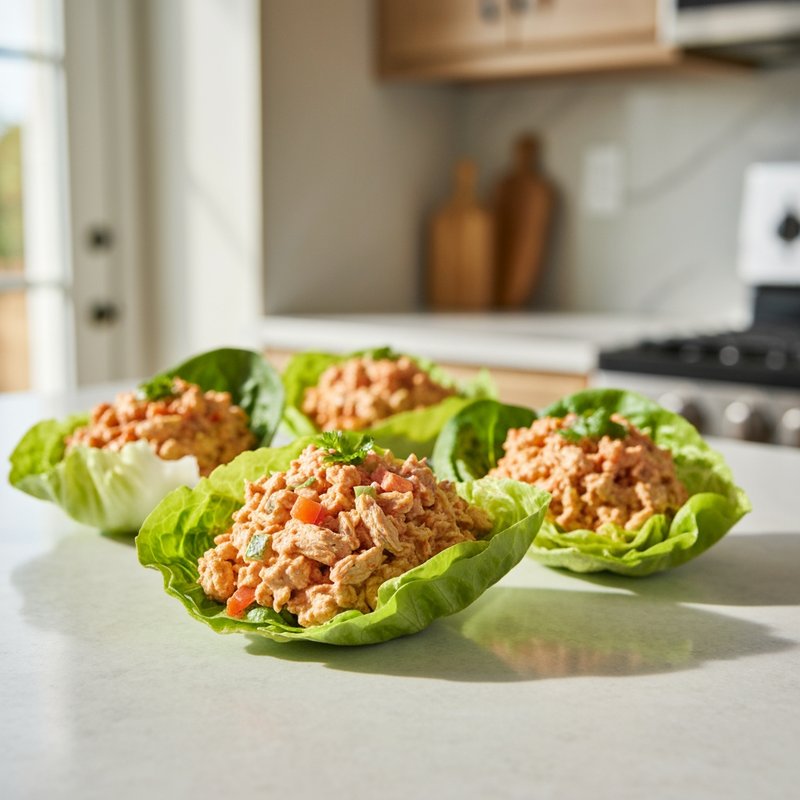
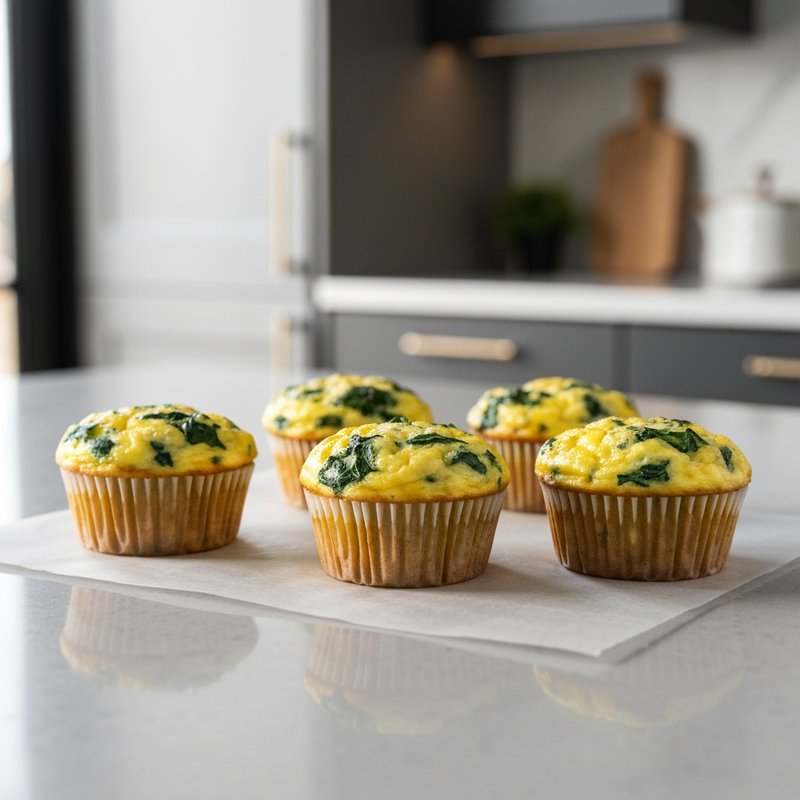
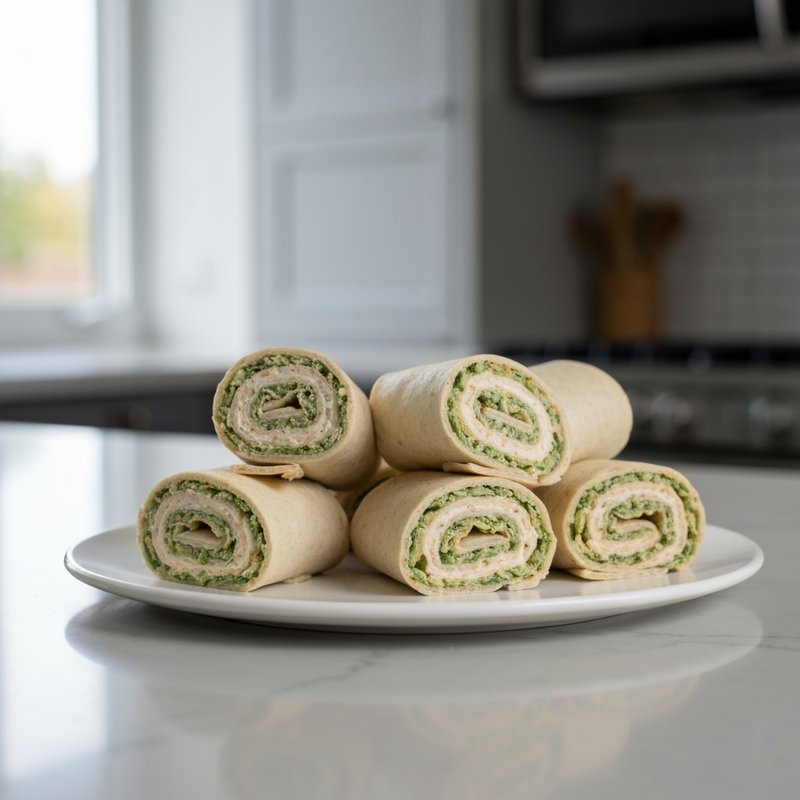
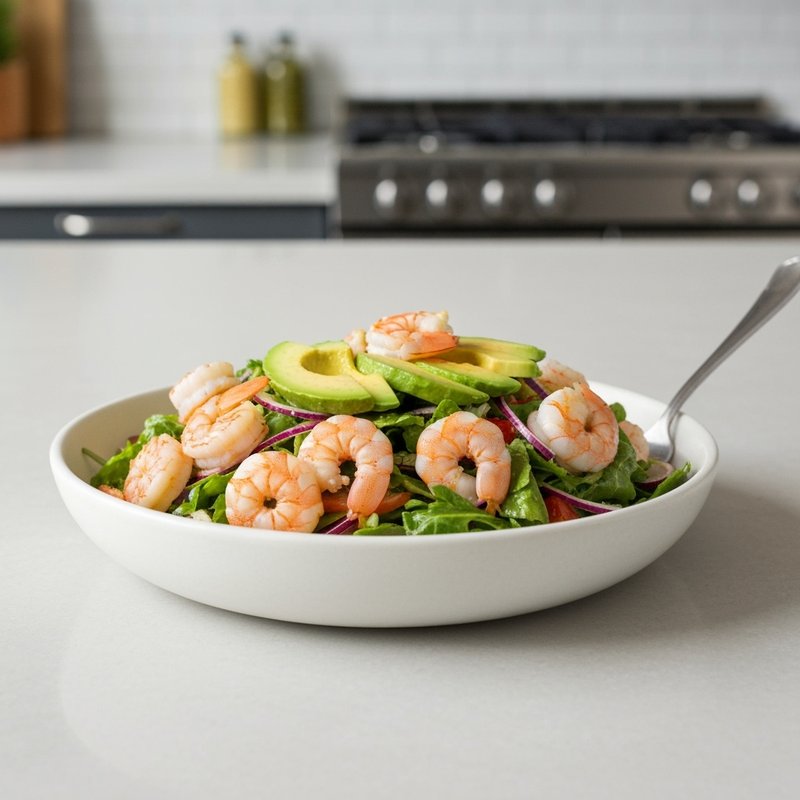
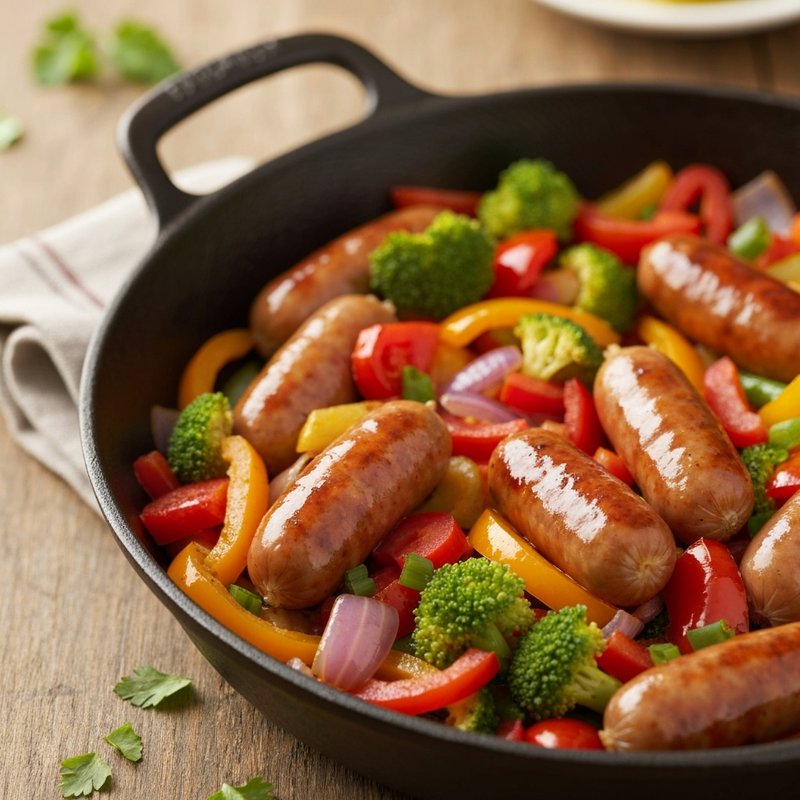
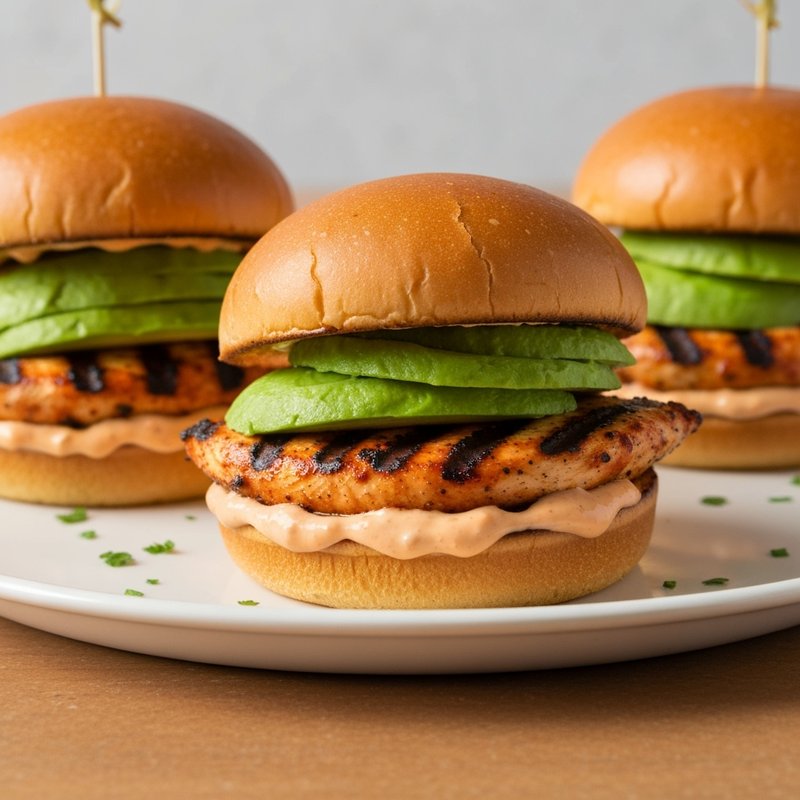
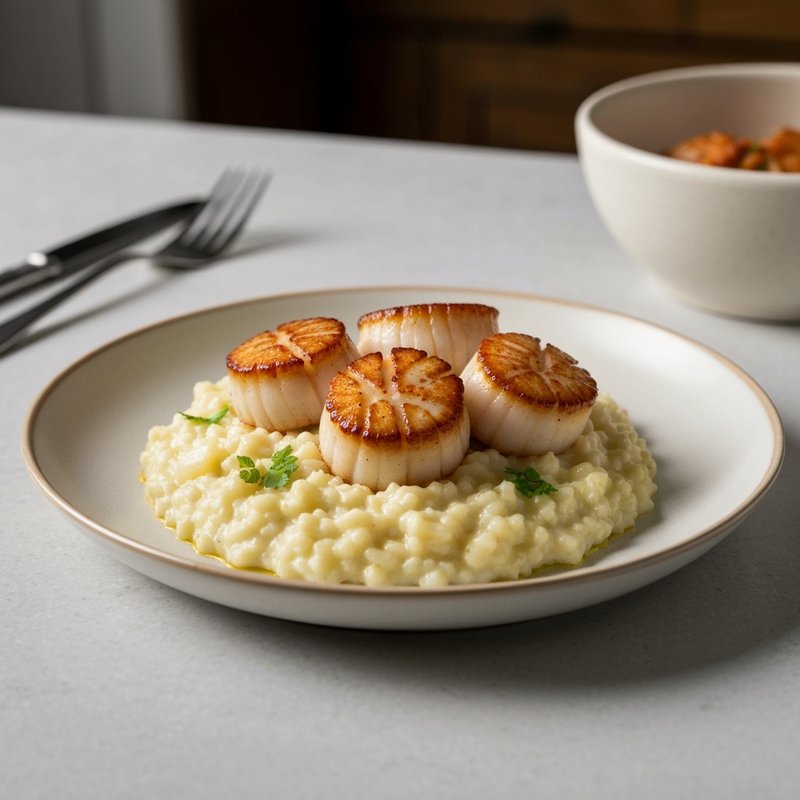
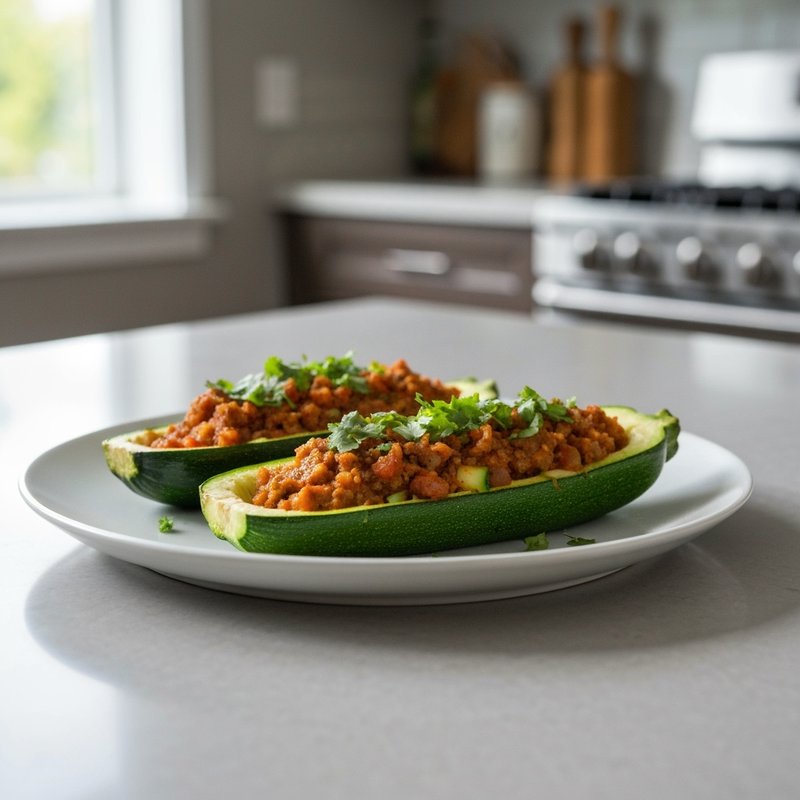
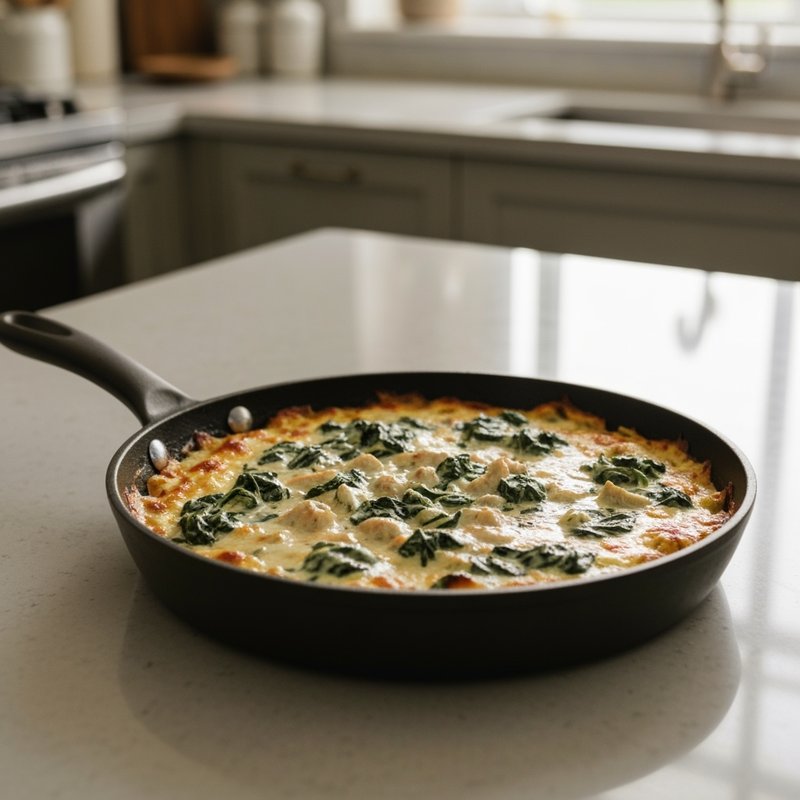
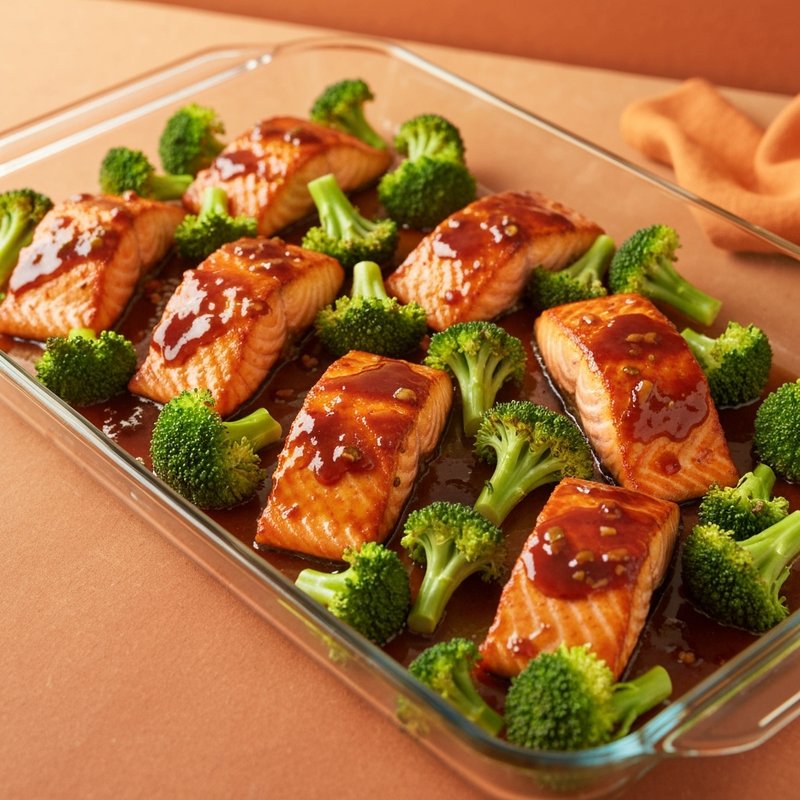
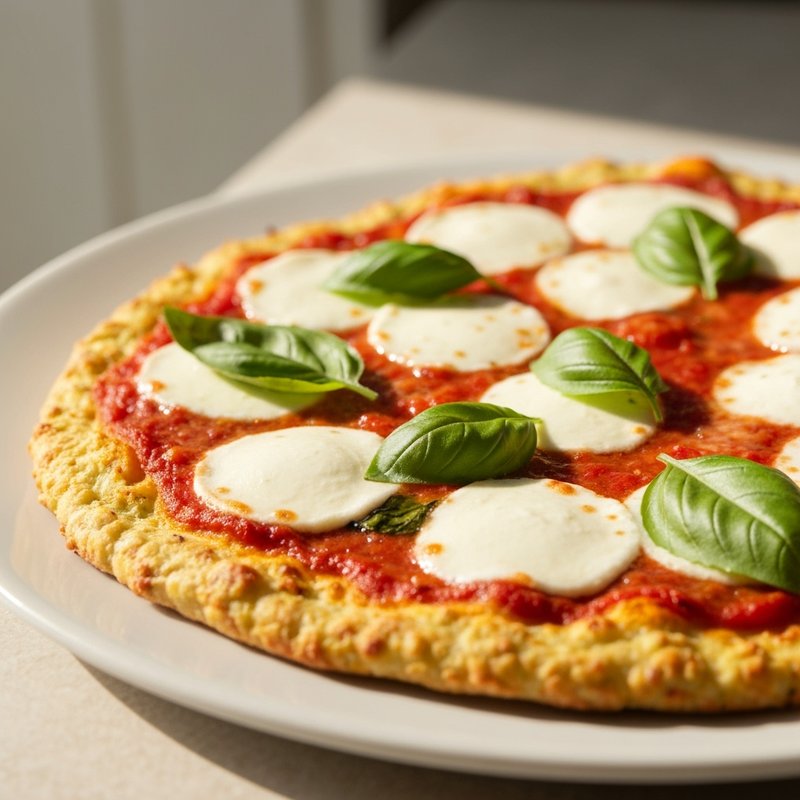
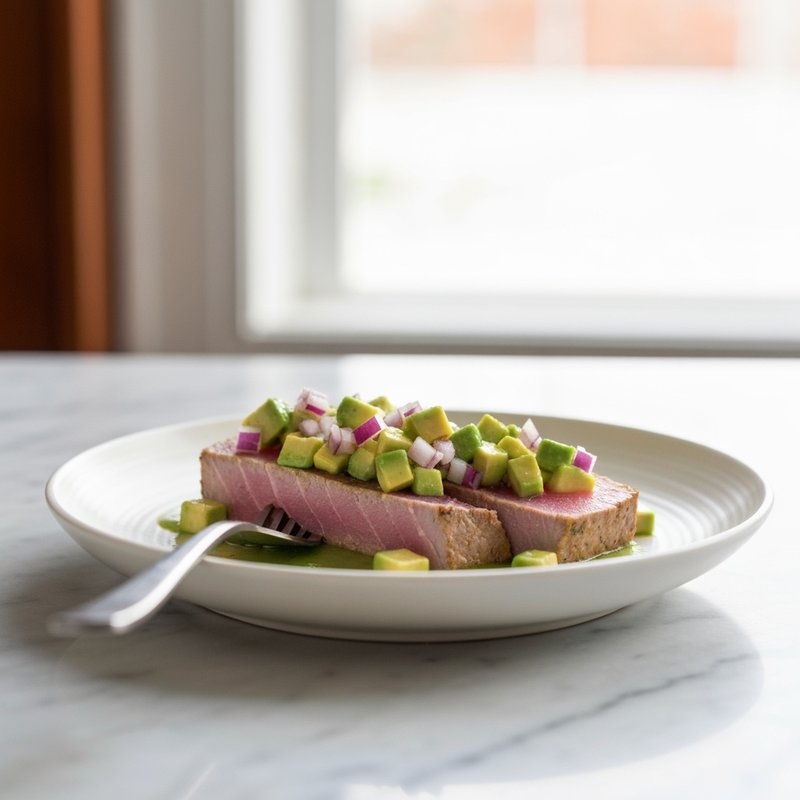
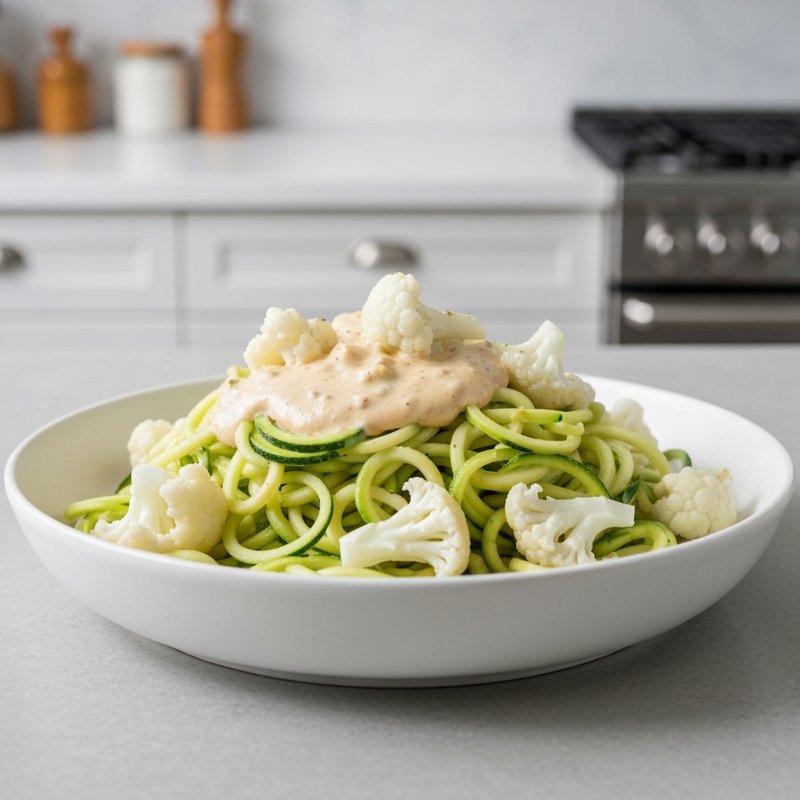
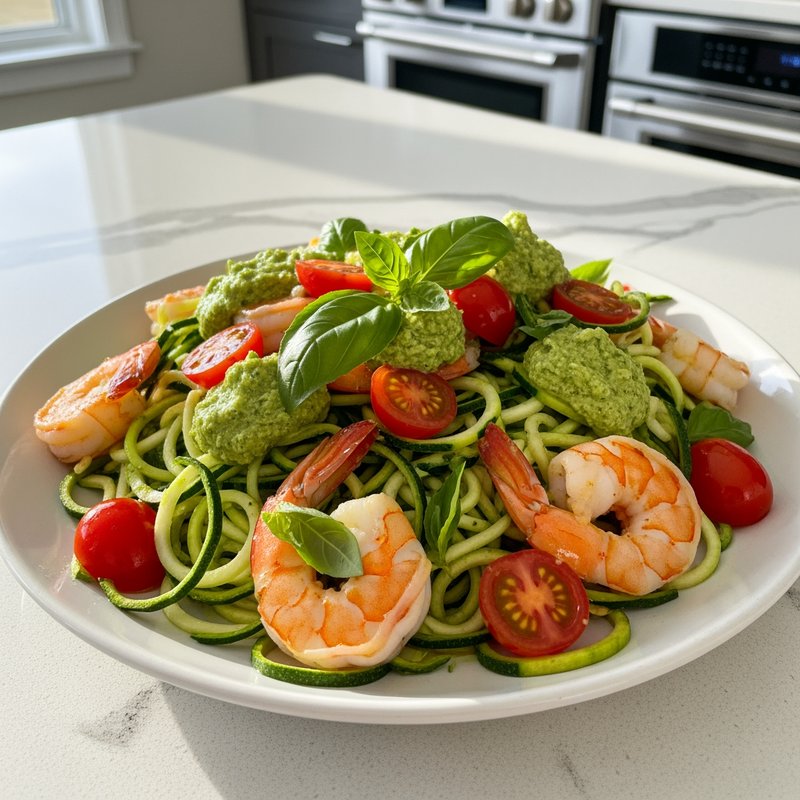
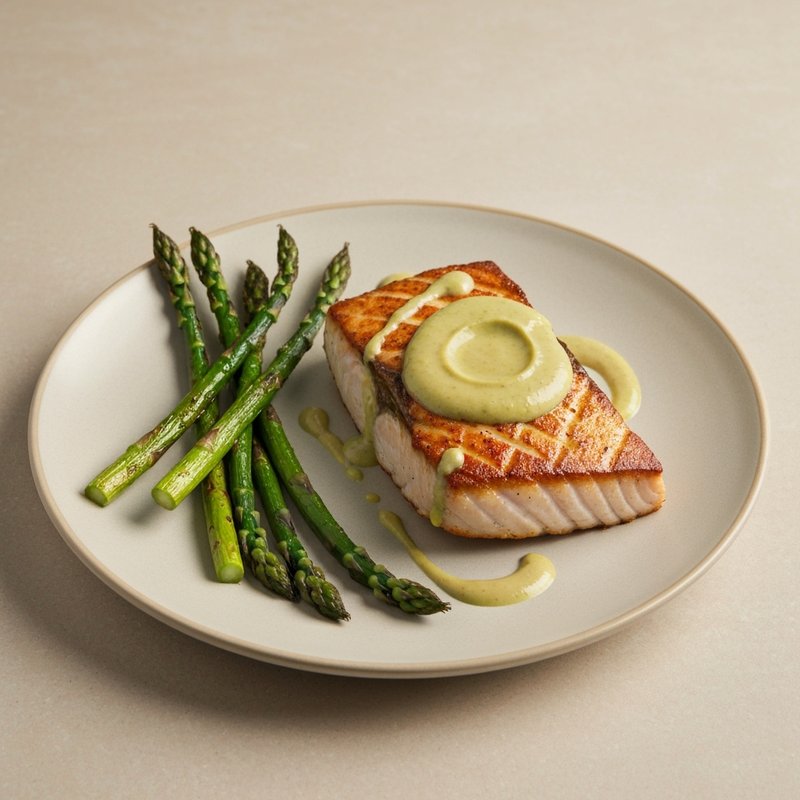
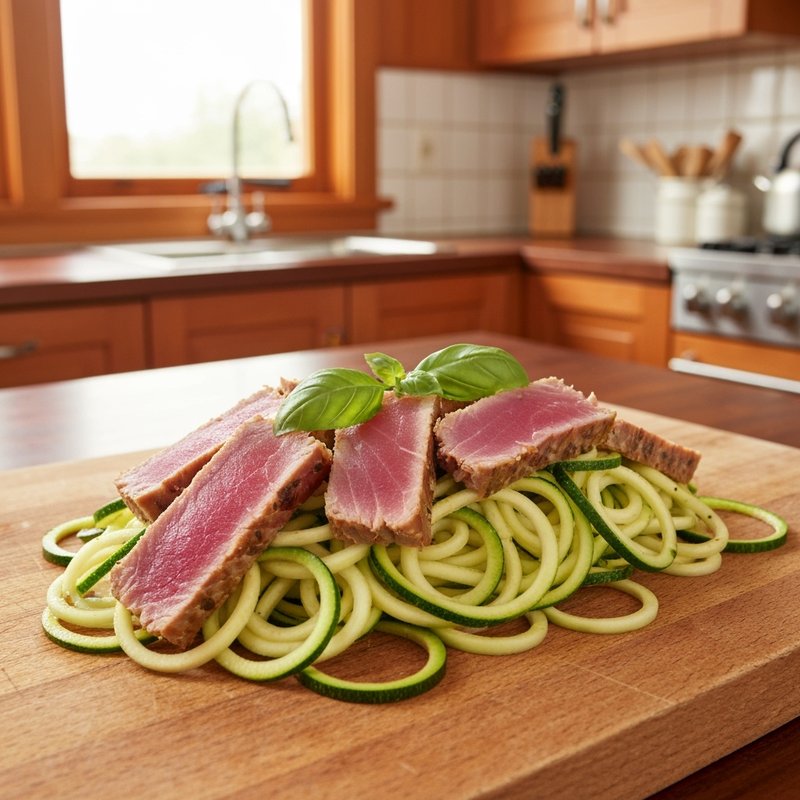
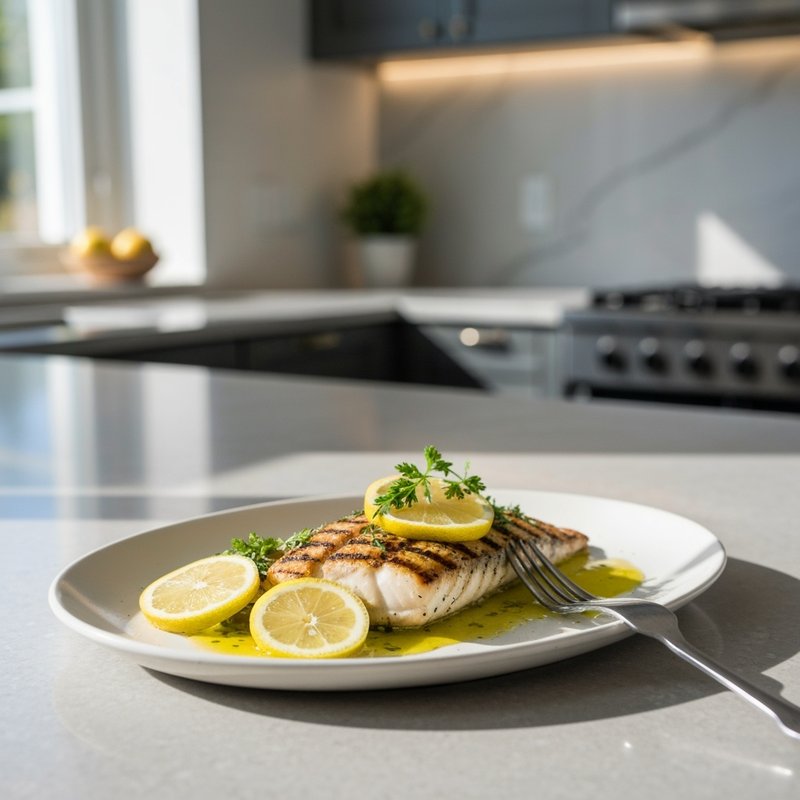
The Ketogenic Diet, commonly known as keto, is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate eating plan designed to shift the body's metabolism into a state called ketosis. In ketosis, the body burns fat for fuel instead of glucose, producing ketones as an alternative energy source. The standard ketogenic diet typically consists of approximately 70-75% of calories from fat, 20-25% from protein, and only 5-10% from carbohydrates, usually limiting net carbs to 20-50 grams per day. This metabolic shift fundamentally changes how the body processes energy and has been associated with numerous health benefits beyond weight loss. Foods emphasized on the ketogenic diet include healthy fats such as avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, butter, and ghee; fatty fish like salmon and mackerel; grass-fed meats and poultry; eggs; full-fat dairy products; nuts and seeds (particularly macadamias, pecans, and almonds); and low-carbohydrate vegetables such as leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, zucchini, and peppers. Foods that must be strictly excluded include all grains and grain products (wheat, rice, oats, corn), sugar and sweetened foods, most fruits (except small portions of berries), starchy vegetables (potatoes, sweet potatoes, corn, peas), legumes and beans, and most processed foods containing hidden carbohydrates. The ketogenic diet was originally developed in the 1920s as a therapeutic treatment for epilepsy and remains a medically supervised intervention for drug-resistant seizures, particularly in children. Modern research has demonstrated its effectiveness for several health conditions, including Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes (by improving insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control), obesity and metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), certain neurological conditions including Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, and reducing inflammation throughout the body. Studies have shown that the diet can lead to significant improvements in triglyceride levels, HDL cholesterol, blood pressure, and markers of inflammation. Some research also suggests potential benefits for certain types of cancer, as cancer cells often rely heavily on glucose for energy. The ketogenic diet may be most beneficial for individuals with insulin resistance, Type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, or those seeking significant weight loss, particularly when other dietary approaches have failed. It's also valuable for people with neurological conditions like epilepsy or those seeking cognitive benefits and mental clarity. However, the diet requires careful planning and may not be suitable for everyone, including pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with certain liver or pancreatic conditions, those with a history of eating disorders, or people taking specific medications. Anyone considering the ketogenic diet, especially those with existing health conditions, should consult with a healthcare provider before beginning, as the dramatic metabolic shift requires proper monitoring and may necessitate medication adjustments.
71 recipes available for this diet