Paleolithic Diet
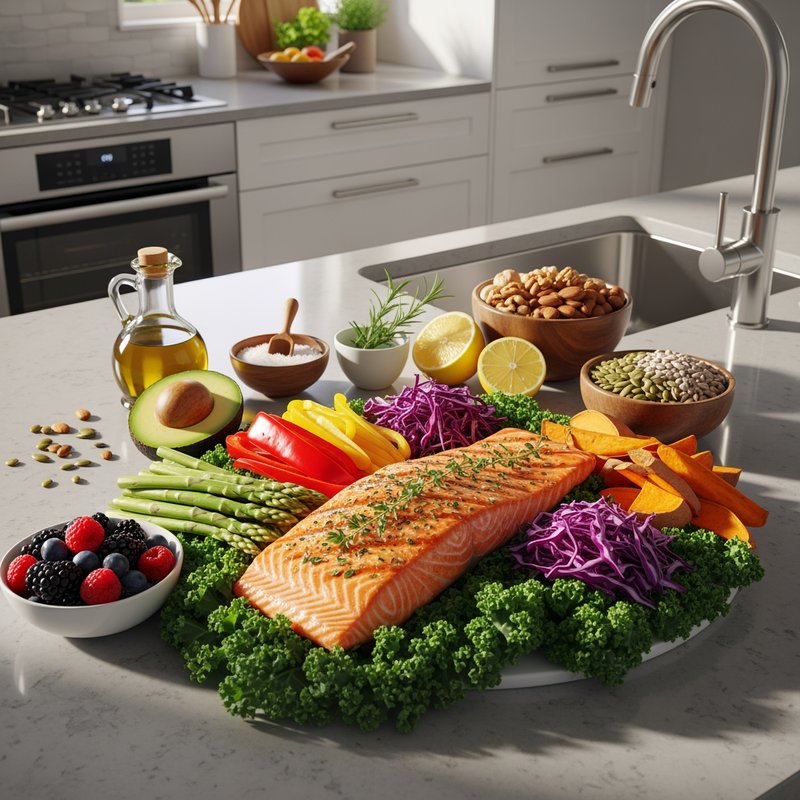
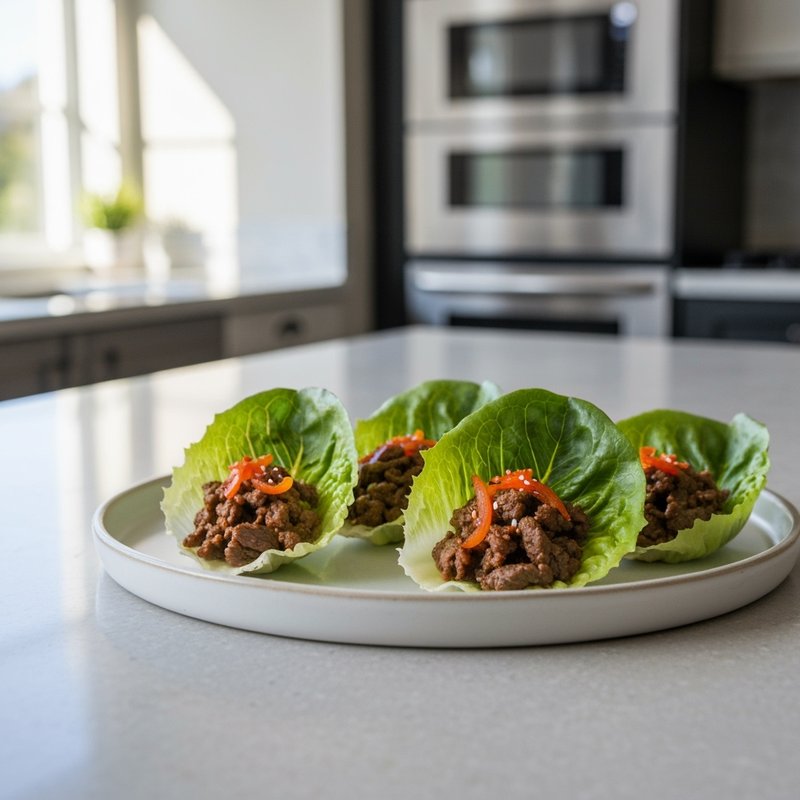
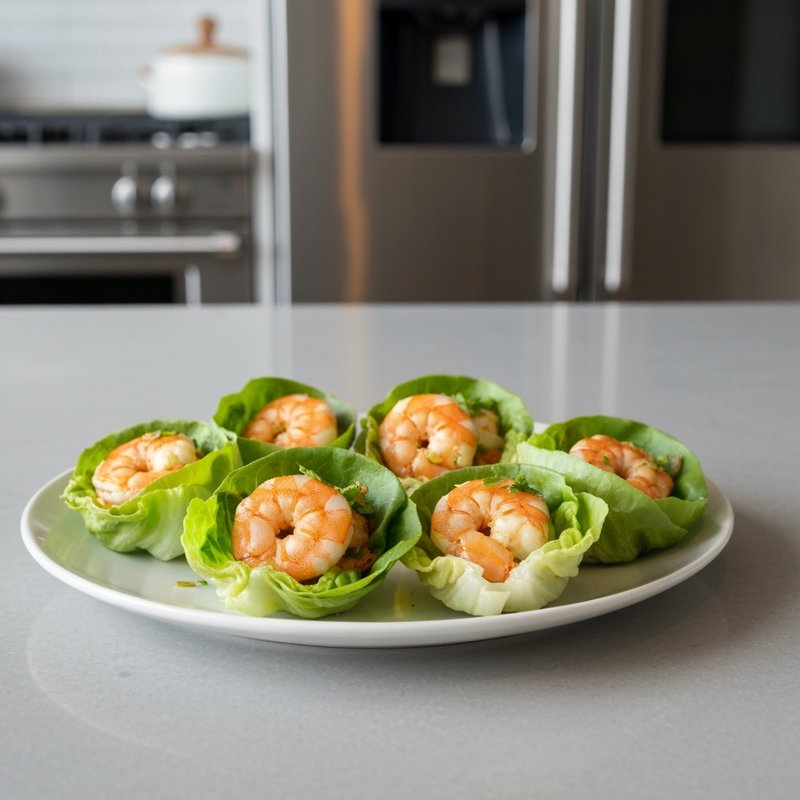
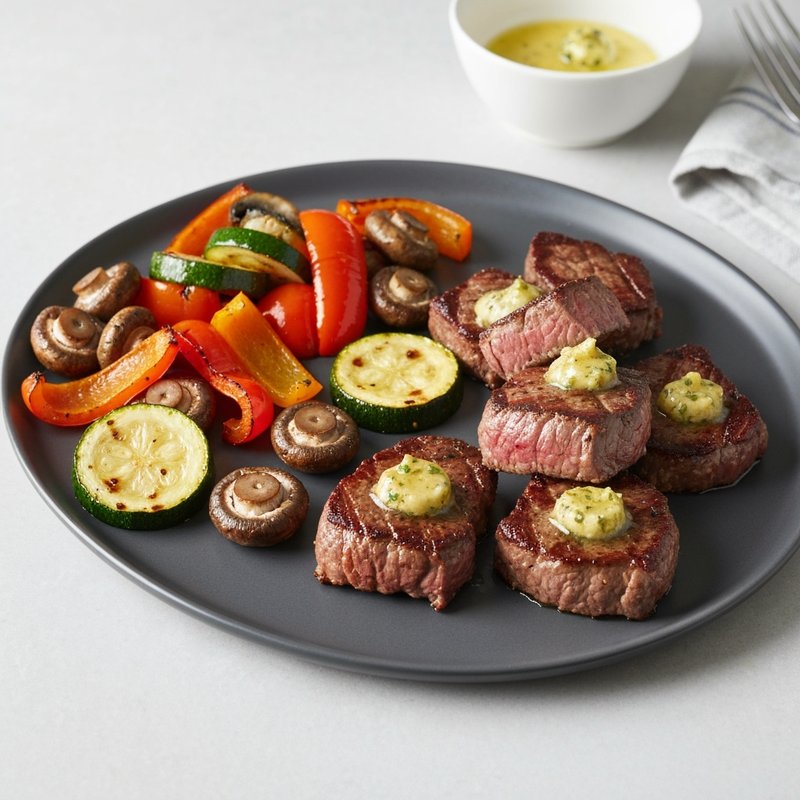
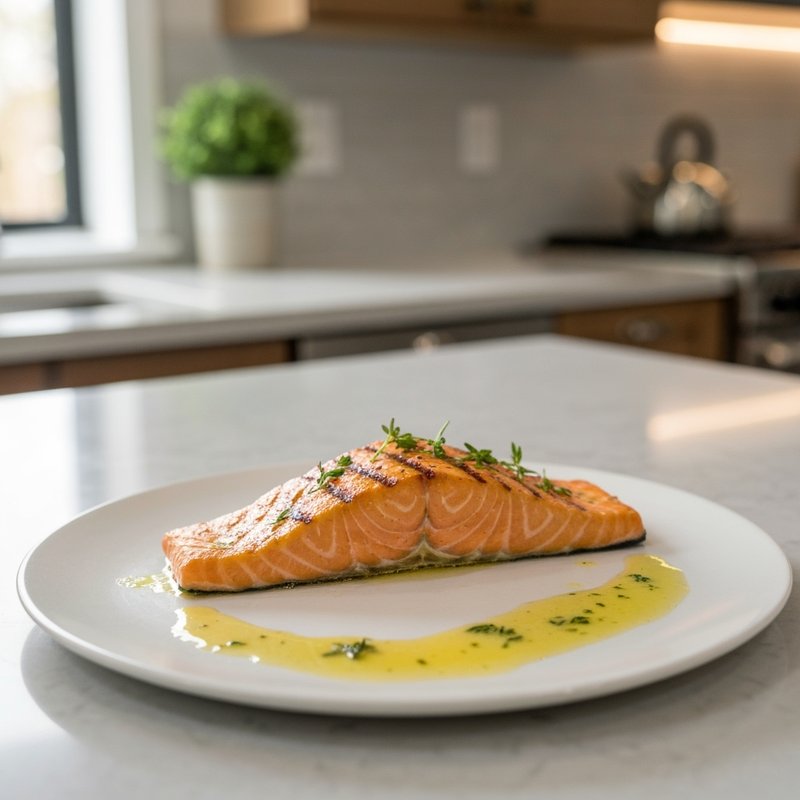
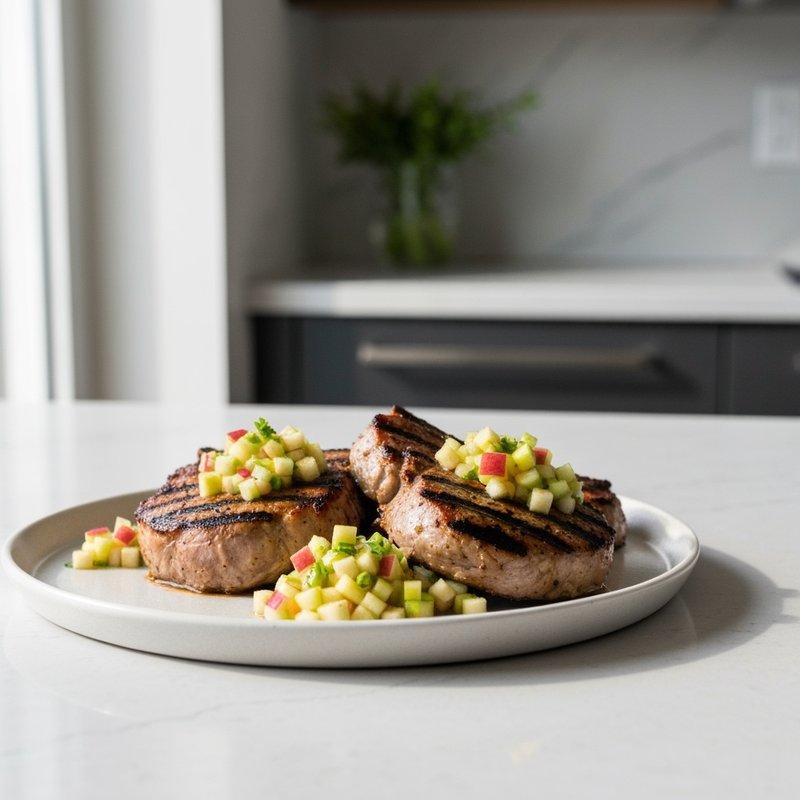
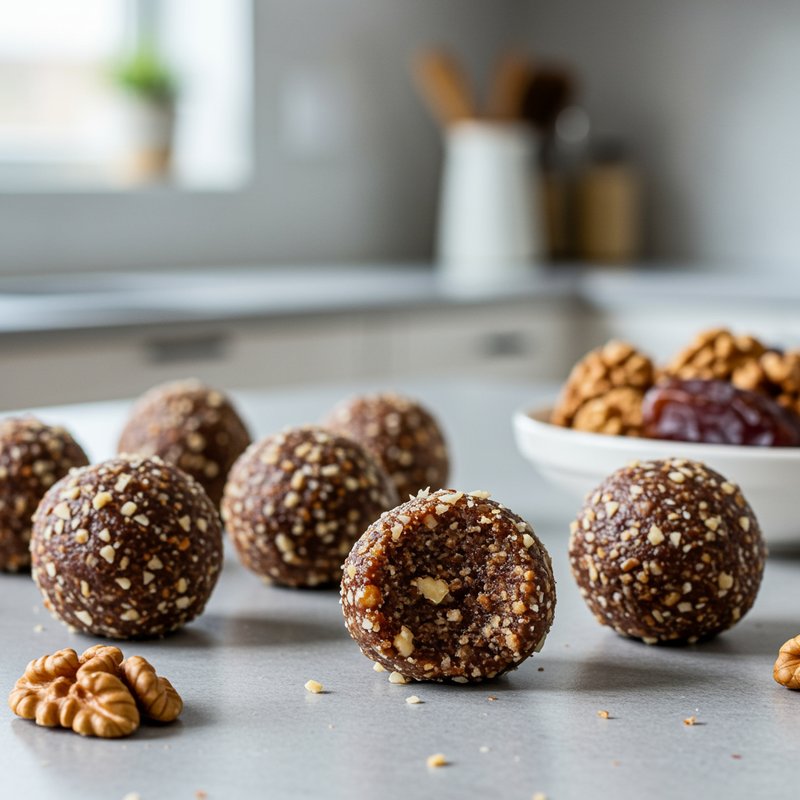
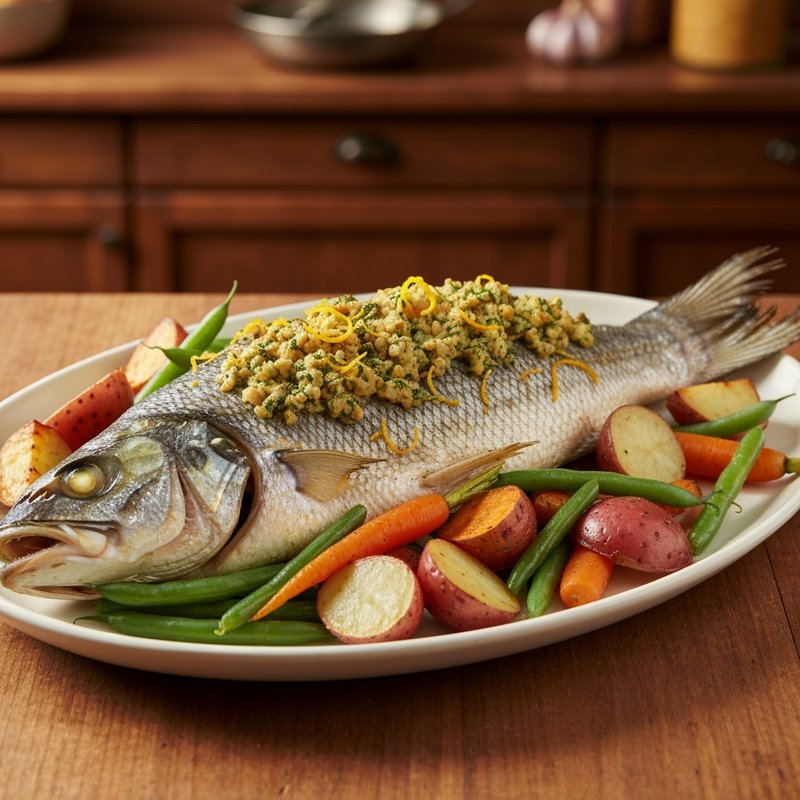
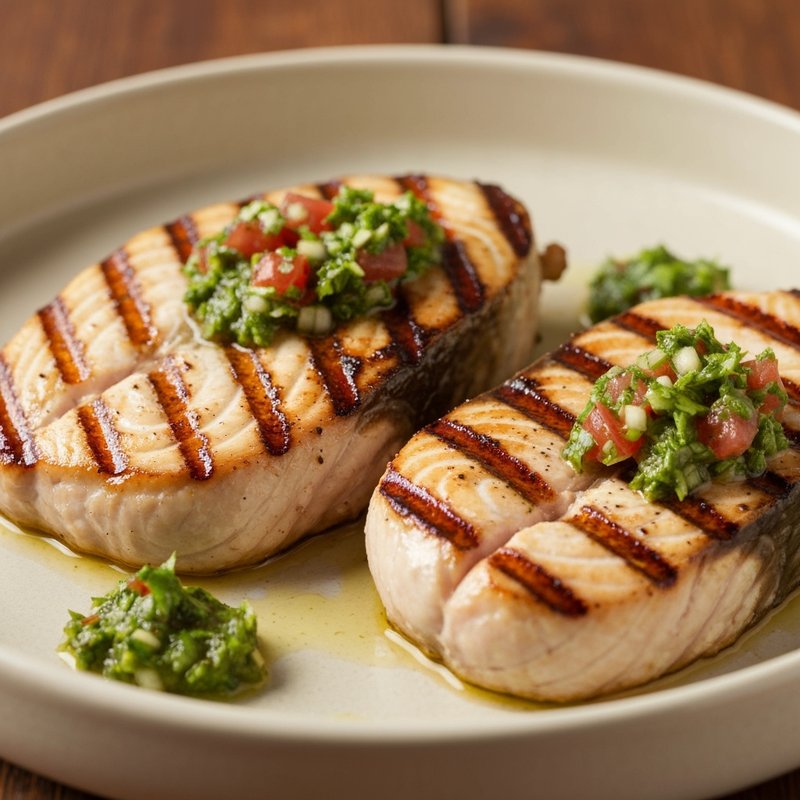
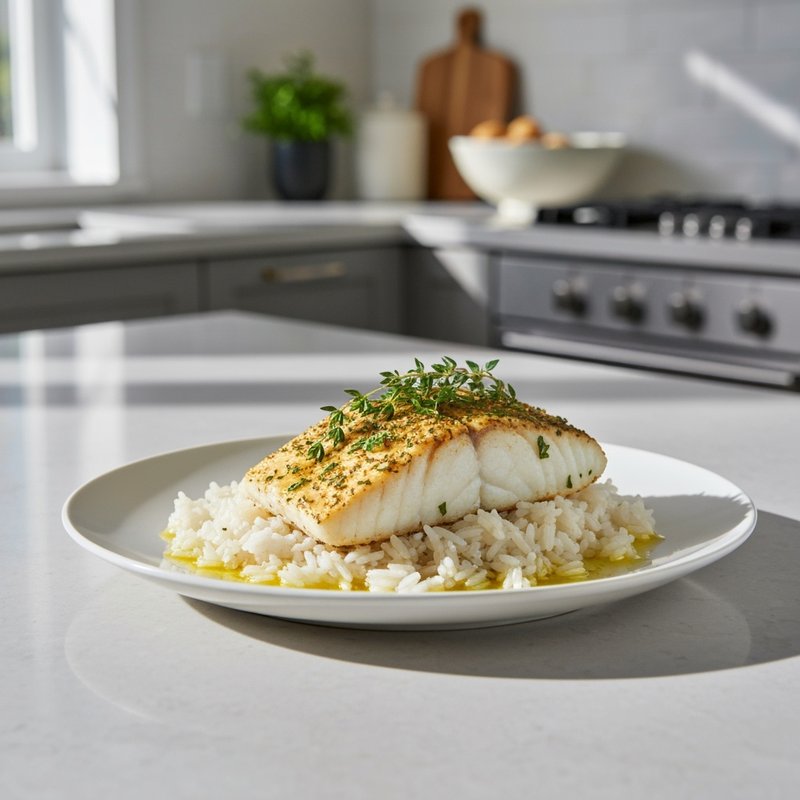
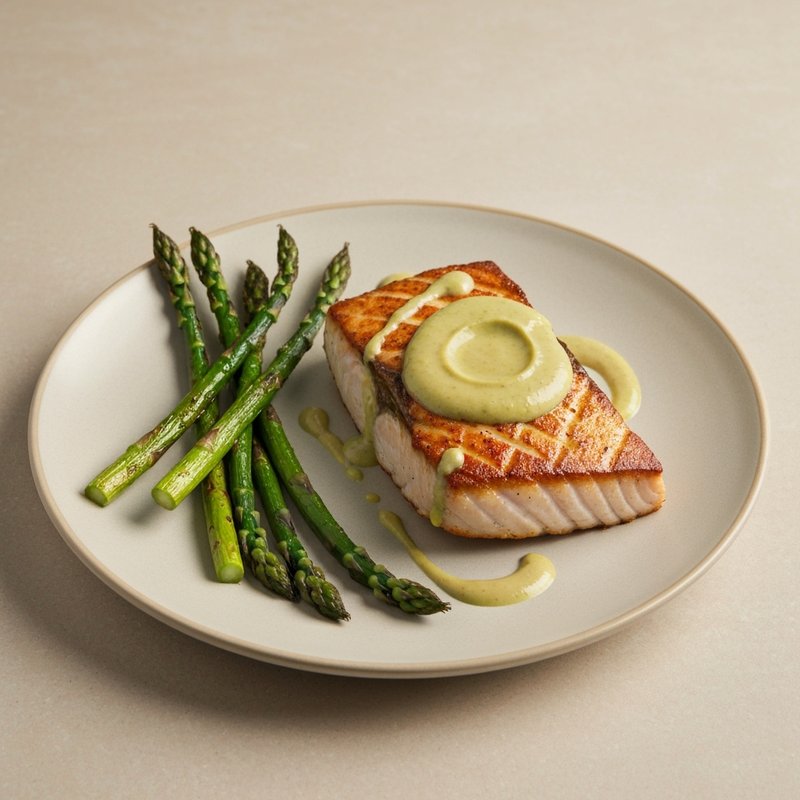
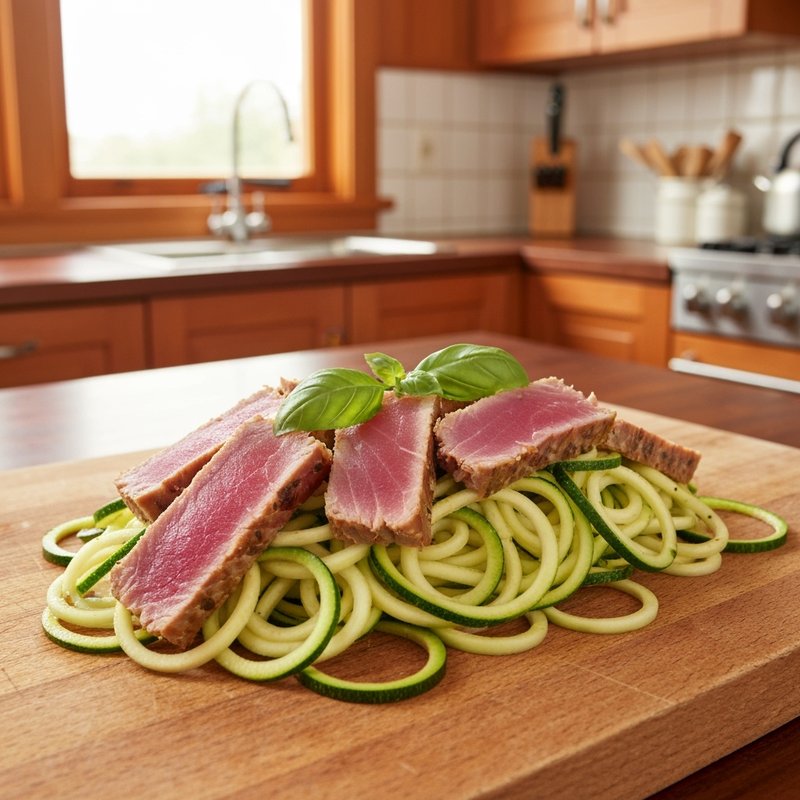
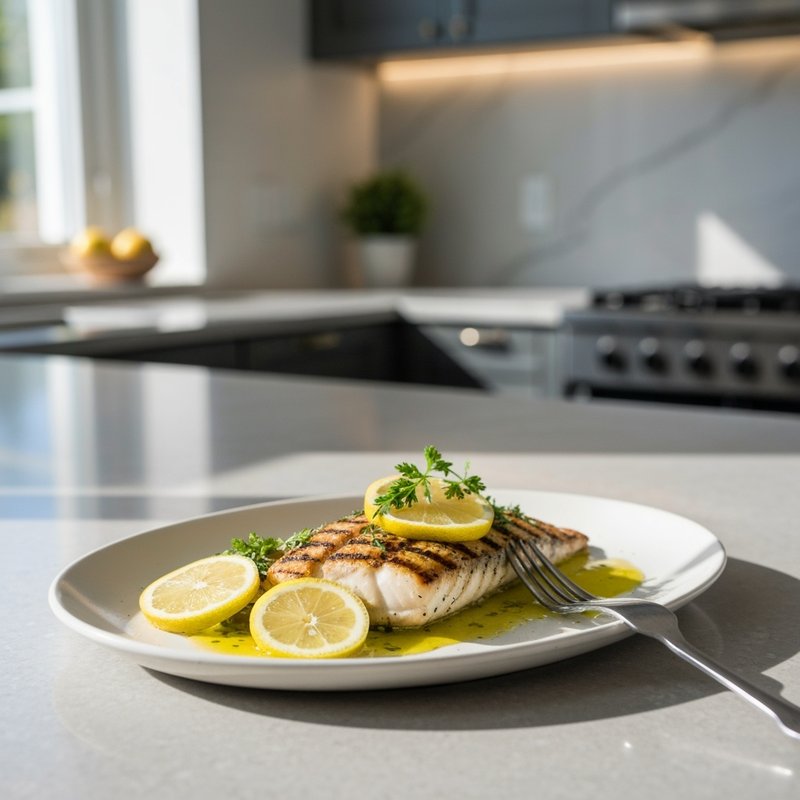
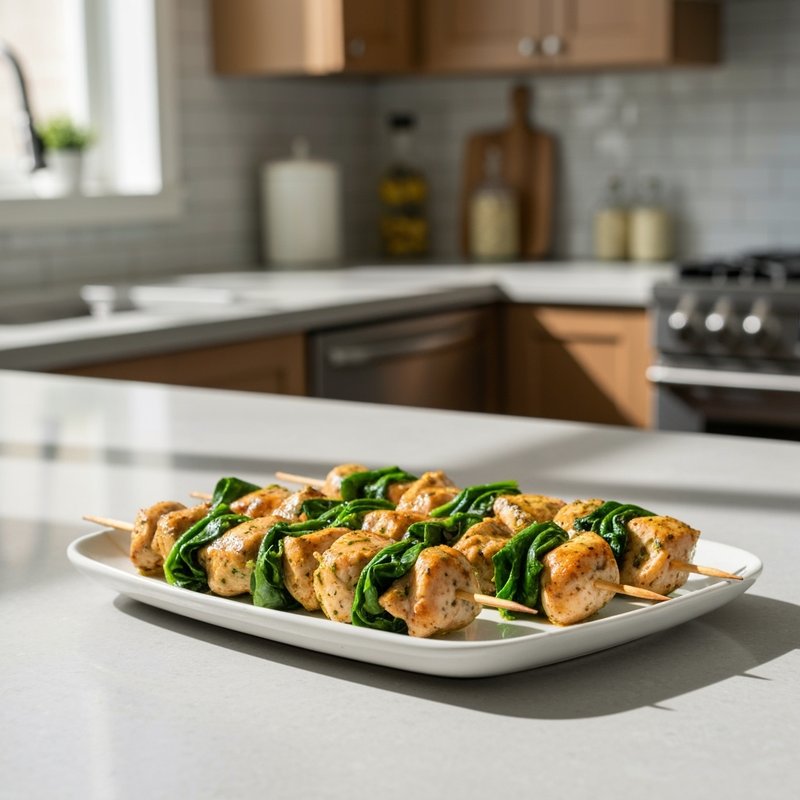
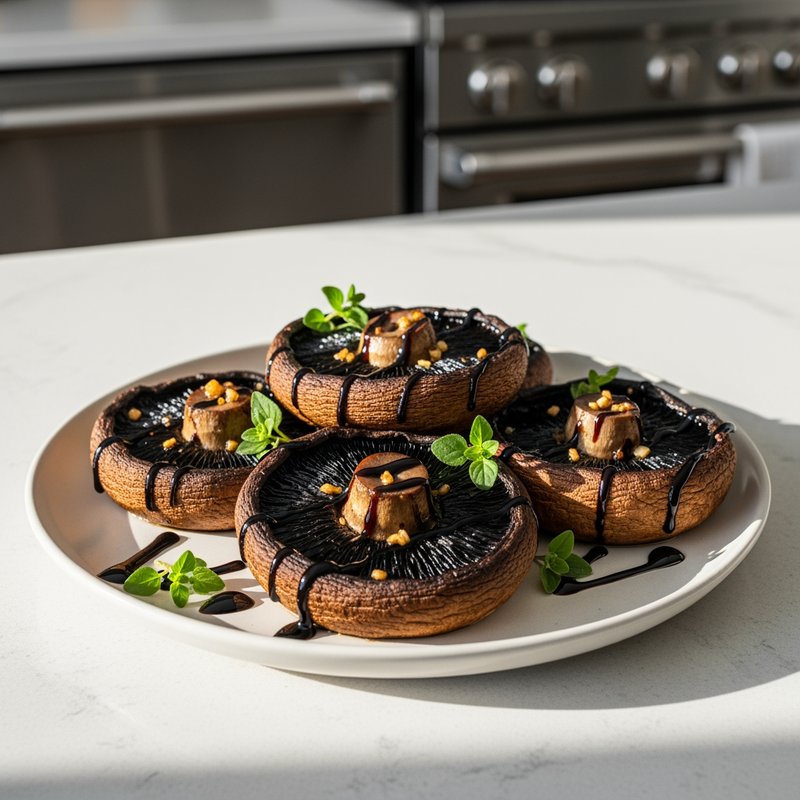
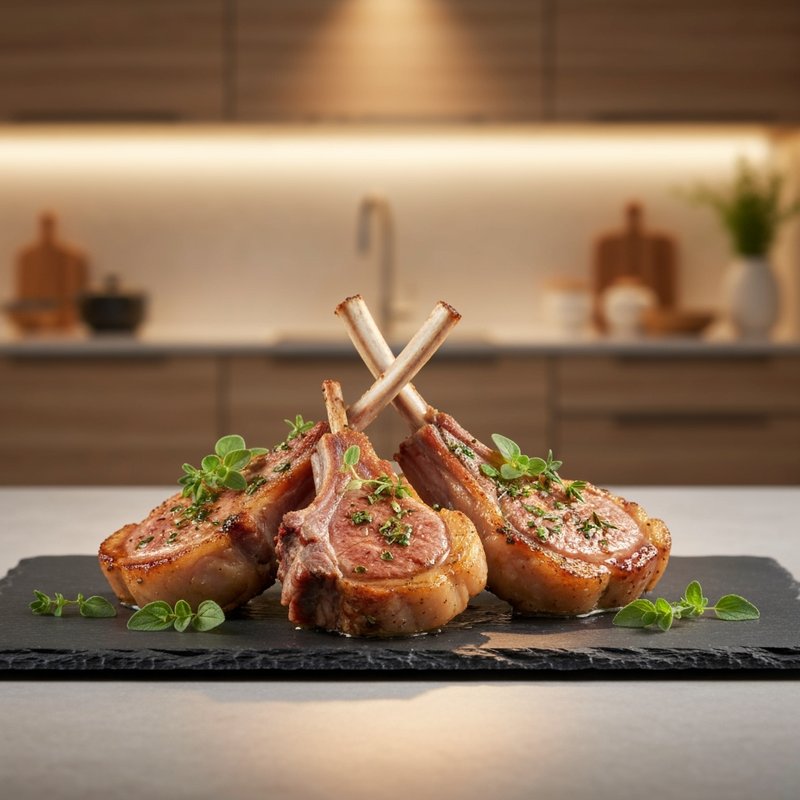
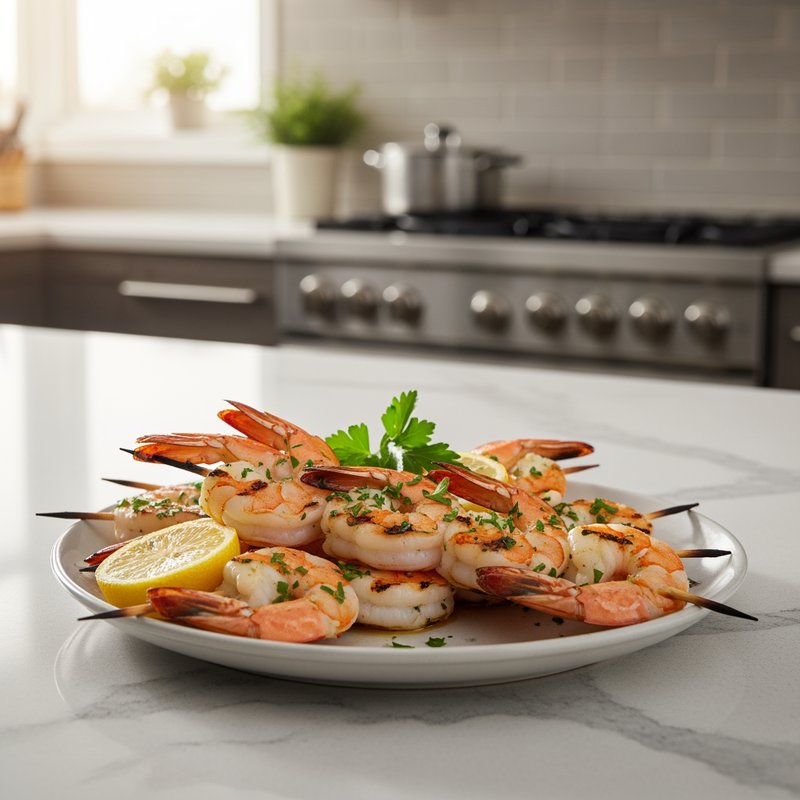
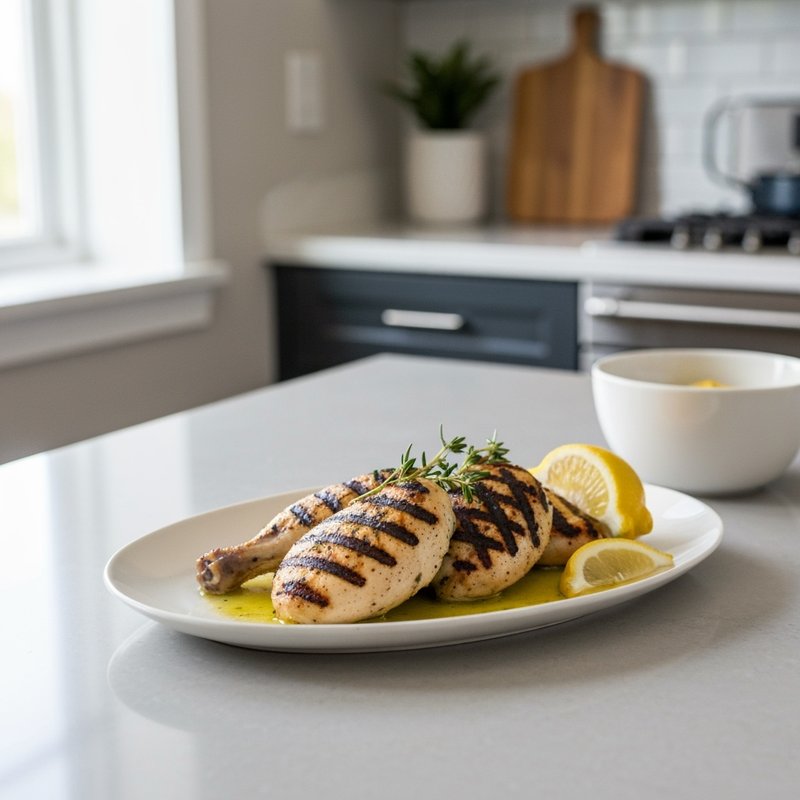
The Paleolithic Diet, commonly known as the Paleo Diet, is a nutritional approach based on the presumed eating patterns of humans during the Paleolithic era, roughly 2.5 million to 10,000 years ago. The core principle is that modern humans are genetically adapted to eat the foods available to our pre-agricultural ancestors, and that many contemporary health problems stem from the mismatch between our genes and modern processed foods. This diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods that could theoretically be obtained through hunting and gathering, while excluding foods that became common only after the development of agriculture and industrial food processing. The Paleo Diet includes grass-fed meats, wild-caught fish and seafood, eggs, vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and healthy oils such as olive, coconut, and avocado oil. It strictly excludes grains (wheat, oats, rice, corn), legumes (beans, lentils, peanuts, soy), dairy products, refined sugar, processed foods, artificial sweeteners, vegetable oils high in omega-6 fatty acids, and most packaged or processed foods. Some variations allow limited amounts of certain foods like grass-fed butter, fermented dairy, or white rice, but the strictest interpretations maintain that these post-agricultural foods should be avoided entirely. Proponents claim the Paleolithic Diet can help address numerous health conditions including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, inflammatory conditions, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome and celiac disease. The diet's elimination of gluten-containing grains makes it naturally suitable for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, while its focus on low-glycemic foods and elimination of refined carbohydrates may help stabilize blood sugar levels in diabetics. The anti-inflammatory properties of the diet, stemming from its emphasis on omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidant-rich vegetables while eliminating processed foods and excess omega-6 oils, may benefit those with chronic inflammation, arthritis, or autoimmune conditions. Several studies have shown potential benefits of the Paleo Diet, including improved glucose tolerance, better blood pressure control, increased satiety, and favorable changes in cardiovascular risk factors. However, the scientific community remains divided, with critics noting the lack of long-term studies, concerns about saturated fat intake, the exclusion of nutrient-rich food groups like legumes and whole grains, and questions about the historical accuracy of the diet's premises. This diet may be most beneficial for individuals with autoimmune conditions, those seeking to reduce inflammation, people with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes, individuals with gluten sensitivity, and those looking to eliminate processed foods from their diet. Athletes and highly active individuals may need to modify the approach to ensure adequate carbohydrate intake for performance.
20 recipes available for this diet